Lasers are complex technology, which can make their specifications and attributes confusing to navigate. To help you better understand key laser product details as you shop, this article will explain the most common terminology in straightforward terms with real-world examples.
Common Laser Light Terms
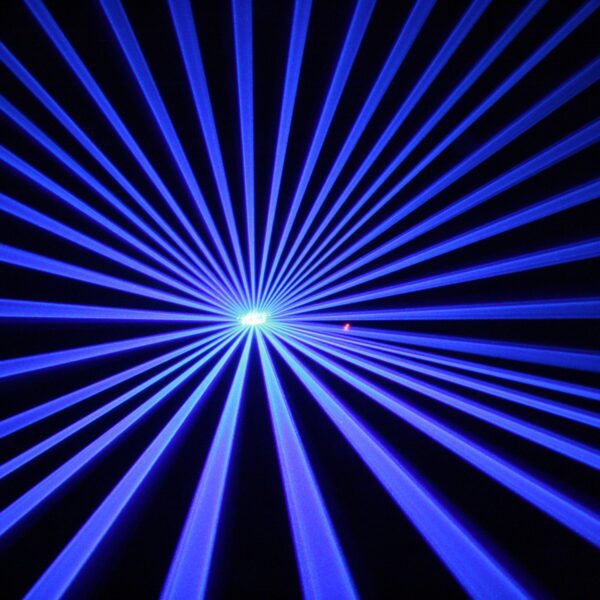
Wavelength and Color
One of the most important laser traits is wavelength, measured in nanometers (nm). This determines the laser’s color. Different wavelengths appear as different visible colors:
- 405nm – Violet
- 532nm – Green
- 638nm – Red
- 445nm – Royal Blue
- 650nm – Deep Red
For multi-color effects, DJ lasers combine multiple wavelengths like red, green, and blue into one unit. Or utilize wavelength mixing to produce a spectrum from a single laser diode.
Scan Rate (KPS)
Scan rate, or KPS, indicates a laser’s scanning speed in kilo scans per second. This determines how fast the unit can project animations and graphics cleanly.
- Low-speed lasers under 4KPS work for simple beam effects.
- High-speed 12KPS+ is best for club environments with complex graphics.
- 20KPS supports very intricate animations like detailed logos or text.
Diode Type
Laser diodes produce the actual laser beam. Key types include:
- IR Diodes for infrared wavelength invisible beams.
- RGB Diodes for red, green and blue visible laser beams.
- Laser Modules which integrate multiple diodes and optics into a single unit.
High-quality diodes from reputable brands like Osram ensure optimal efficiency and brightness.
Scanner Type
The scanner directs and controls laser beam motion through mirrors:
- Galvo Scanners steer beams rapidly with micro mirror movement for graphics.
- Polygon Scanners use rotating optics for faster and more complex effects.
- Hybrid Scanners combine both for versatility.
Higher quality mirrors enable faster scan rates and accuracy.
Optical Power
This indicates the diode’s power output, measured in milliwatts (mW). More power means brighter projection:
- Low power: <100 mW Class 3R lasers
- Mid power: 100-499mW Class 3B lasers
- High power: 500mW+ Class 4 lasers
Venue size and ambient light determine ideal power needs.
Beam Count
Multiple laser diodes can project different color beams simultaneously. Beam count indicates how many are in one unit. For example, a 3 beam laser has separate red, green and blue lasers.
Higher beam counts allow for more vibrant, complex effects but at increased cost. Three or five beams provide a good balance for most DJs.
Control and Programming
Beyond manual control knobs, common laser programming options include:
DMX Control – Connect lighting consoles to choreograph laser shows, synchronize motions to music, integrate with stage lighting.
ILDA – Project graphics, text, and animations using PC-driven laser show control software.
Standalone – Built-in show modes like sound activation and automatic patterns.
Consider needs and technical skill when weighing programming choices.
Key Takeaways
While laser terminology can seem complex initially, the key specifications like wavelength, scan rate, power output, and control modes tell you exactly what a laser can do. Understanding these traits allows picking the perfect laser for your DJing needs.
We hope this breakdown demystifies laser terminology to make your buying choice clearer. Let us know if you need any guidance selecting professional lasers to enhance your events!